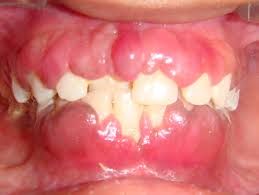
Medications Cause Gums Enlargment
Several causes of gingival enlargement are known, and the most recognized is drug-induced gingival enlargement .Gum enlargement can reach some times to extents that can cause difficulty in chewing if it is allowed to advance. Moreover, the enlarged and misshapen gums make effective tooth cleaning impossible and promotes plaque to accumulate, resulting in gum inflammation(gingivitis), and tooth supporting tissue destruction (periodontitis) ending up with tooth loss.
Drugs involved are:
-Antiseizure medications (eg. epilepsy)
-Immunosuppressant medications (used after organ transplantations) .
-Calcium channel blockers (for cardiovascular conditions e.g. blood pressure)
In this article well be discussing about Immunosuppressant medications and blood pressure medications.
Immunosuppressant medications
A also called anti-rejection drugs, used to prevent rejecting a transplanted organ. When an organ, such as liver, heart or kidney, is transplanted from a donor into the recipient, despite close matching of the donated organ and the transplant patient the immune system of the recipient triggers the same response against the new organ it would have to any foreign body, setting for events that can damage and reject the transplanted organ. This rejection can be rapid (acute rejection), or over a long period of time (chronic rejection).
Immunosuppressant drugs dramatically decrease the risks of rejection, protecting the new organ . These drugs act by blocking the natural immune system of the body.
Immunosuppressant drugs are also used to treat some other diseases termed “autoimmune” diseases( immune system is acting against the body itself).
Classification:
The three main immunosuppressant drugs used in organ transplantations are :
i.Cyclosporins (Neoral, Sandimmune, SangCya). used since the early 1980s Act by inhibiting T-cell activation, thus preventing T-cells from attacking the transplanted organ.
ii.Azathioprines (Imuran). These drugs disrupt the synthesis of DNA and RNA and cell division.
iii.Corticosteroids such as prednisolone (Deltasone, Orasone). These drugs suppress the inflammation associated with transplant rejection
Most patients are prescribed a combination of medicines after transplant, one from each of the above main groups. Over a period of time, the doses and number of drugs taken may be reduced as the risks of rejection decrease. However, majority of patients need to take at least one immunosuppressive for the rest of their lives.
High blood pressure medications and gum People diagnosed with high blood pressure, are likely to take antihypertensive medications for long time. One class of antihypertensive medications, known as calcium antagonists – for eg. nifedipine, amlodipine and felodipine – can cause overgrowth of gums in some individuals.
Physical
Gingival enlargement occurs primarily on the labial gingival mucosa and in between the teeth (interdental papillae area) but also in the lingual gingival as well. Gingival overgrowth is more pronounced in the maxillary gingiva and in between teeth.
Measures to minimize the onset and severity of gingival overgroth
Although medications may be responsible for causing the growth in size and shape of the gums, but the ineffective cleaning resulting in accumulation of dental plaque around the teeth remains the most important factor in gum growth, as the inflammatory changes are provoked by periodontal bacteria. Moreover, gum overgrowth tends to be worse in areas where bacteria accumulate readily and this usually begins in between the teeth. The overgrown areas then become even more difficult to clean because of the extra gum tissue and growth becomes even more.
Effective plaque removal is therefore the corner stone in limiting the gum overgrowth and preventing inflammation, tissue destruction and at the end tooth mobility and loss. their for our advice is:
Daily home care it is essential that you maintain a regular and thorough oral hygiene routine at home, including tooth brushing and interdental cleaning, with small brushes or floss.. Fluoridted toothpastes, mouthwashes eg. Chlorhexidine gluconate(12%) or Biotene are mandatory. Patients should practice thorough oral hygiene twice a day (i.e., before breakfast, before going to bed) and rinse mouth with plain water after each meal .
Three months dental checkups Professional tooth cleaning regularly every 3 months is mandatory. at these visits, all soft and hard deposits are removed and your oral hygiene practices are reviewed and adjusted if necessary. These measures are often successful in reducing mild overgrowth of the gums and will help prevent further enlargement.
Changing medication or dosage
After consulting with physician responsible for your prescription, sometimes it is possible to alter the dosage of medication or switching to an alternative medication. Experiments proof that gingival overgrowth was reduced after switching from cyclosporine A to tacrolimus.
Antibiotic
Clinical studies combining practicing oral hygiene care and the use of azithromycin significantly reduce cyclosporine-induced gingival over growth, while oral hygiene alone reduces oral symptoms but does not affect cyclosporine gingival over growth.
Surgical Care
Finally surgical excision of gingival tissue remains the only treatment option recommended for patients who have moderate-to-severe gingival enlargement that does not resolve when the dose is reduced, proper oral hygiene is maintained, or after a short course of antibiotics. Internal beveled gingivectomy is favored over the conventional gingivectomy , owing to the predictable healing and better esthetics.
Leave a reply →
Leave a reply